caliper gauge
A caliper gauge, also known simply as a caliper, is a versatile precision measuring instrument used to determine the distance between two opposing sides of an object. It's essential for achieving accuracy in various fields, including engineering, manufacturing, woodworking, and even jewelry making. They come in different types and offer varying levels of precision, making them a valuable tool for professionals and hobbyists alike.Understanding the Basics of Caliper GaugesWhat is a Caliper Gauge?A caliper gauge is a handheld instrument designed to accurately measure lengths, diameters, and depths. It typically consists of a main scale with a sliding jaw and a fixed jaw. By closing the jaws around the object being measured, the distance between the jaws can be read directly from the scale.Types of Caliper GaugesThere are primarily three types of caliper gauges: vernier, dial, and digital. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of readability, accuracy, and ease of use. Vernier Caliper: The vernier caliper gauge uses a vernier scale to provide precise measurements. It requires some skill to read accurately but is known for its robustness and affordability. Dial Caliper: A dial caliper gauge features a dial indicator that displays the measurement, making it easier to read than a vernier caliper. It's a good balance between accuracy and ease of use. Digital Caliper: Digital caliper gauges offer the most straightforward reading with a digital display. They often include features like zeroing and unit conversion, making them highly convenient.Key Features to Consider When Choosing a Caliper GaugeMeasurement Range and AccuracyThe measurement range of a caliper gauge refers to the maximum distance it can measure. The accuracy indicates how close the measured value is to the true value. Choose a caliper gauge with a range suitable for your typical projects and an accuracy that meets your precision requirements. Many digital calipers, such as those provided by quality suppliers like Wayleading Tools, offer accuracy down to 0.001 inches.Material and DurabilityThe material of the caliper gauge affects its durability and resistance to wear and tear. Stainless steel is a common choice for its corrosion resistance and longevity. Ensure that the caliper gauge is robust enough to withstand regular use in your working environment.Resolution and ReadabilityThe resolution refers to the smallest increment that the caliper gauge can display. Higher resolution allows for more precise measurements. Consider the readability of the scale or display, especially if you need to take measurements quickly and accurately. Digital calipers generally provide the easiest readability.Functions and FeaturesSome caliper gauges come with additional functions, such as: Zeroing: Allows you to set the caliper gauge to zero at any point, useful for comparative measurements. Unit Conversion: Switches between inches and millimeters. Hold Function: Freezes the measurement on the display. IP Rating: Indicates the level of protection against dust and water.Using a Caliper Gauge: A Step-by-Step GuidePreparing for MeasurementBefore using a caliper gauge, ensure that it is clean and free from any debris. Calibrate the caliper gauge if necessary, following the manufacturer's instructions. For digital calipers, ensure that the battery is adequately charged.Measuring External Dimensions Open the jaws of the caliper gauge wider than the object you want to measure. Place the object between the jaws. Close the jaws until they gently touch the object. Read the measurement from the scale or display.Measuring Internal Dimensions Insert the internal measuring jaws into the hole or opening. Open the jaws until they touch the inner walls of the object. Read the measurement from the scale or display.Measuring Depth Place the depth rod against the surface from which you want to measure the depth. Extend the rod until it touches the bottom of the hole or recess. Read the measurement from the scale or display.Applications of Caliper GaugesEngineering and ManufacturingCaliper gauges are essential tools in engineering and manufacturing for quality control, ensuring that parts meet the required specifications. They are used to measure the dimensions of components, verify tolerances, and inspect finished products.WoodworkingIn woodworking, caliper gauges are used to measure the thickness of wood, the diameter of dowels, and the depth of mortises. Accurate measurements are crucial for creating precise and well-fitting joints.Jewelry MakingJewelers use caliper gauges to measure the size of gemstones, the thickness of metal sheets, and the diameter of wires. Precise measurements are essential for creating high-quality jewelry.Maintenance and CareCleaningRegularly clean your caliper gauge with a soft cloth to remove dust and dirt. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners, as they can damage the instrument. A mild solvent can be used to remove stubborn residue.StorageStore your caliper gauge in a protective case or pouch to prevent damage. Keep it in a dry and clean environment, away from extreme temperatures and humidity.CalibrationPeriodically calibrate your caliper gauge to ensure its accuracy. The frequency of calibration depends on the usage and the required level of precision. You can use gauge blocks or other known standards to check the accuracy of your caliper gauge. For professional use, consider sending your caliper gauge to a certified calibration laboratory.Troubleshooting Common IssuesInaccurate ReadingsIf you are getting inaccurate readings, check the following: Ensure that the caliper gauge is clean and free from debris. Verify that the caliper gauge is properly calibrated. Check the battery level of digital calipers. Make sure you are using the correct measuring technique.Sticky or Stiff MovementIf the jaws are sticky or stiff, apply a small amount of light machine oil to the sliding parts. Work the jaws back and forth to distribute the oil evenly.Caliper Gauge Comparison Table Type Accuracy Readability Features Typical Cost Vernier ±0.001 inch Requires practice Simple, robust Low Dial ±0.001 inch Easy to read Good balance of accuracy and ease of use Medium Digital ±0.0005 inch Very easy to read Zeroing, unit conversion, hold function High Choosing the right caliper gauge depends on your specific needs and budget. Consider the factors discussed in this guide to make an informed decision and ensure accurate and reliable measurements for your projects. Remember to source your tools from reputable suppliers like Wayleading Tools, known for their quality and precision.*Disclaimer: Accuracy values are typical and may vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer. Always refer to the product specifications for accurate details.*
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
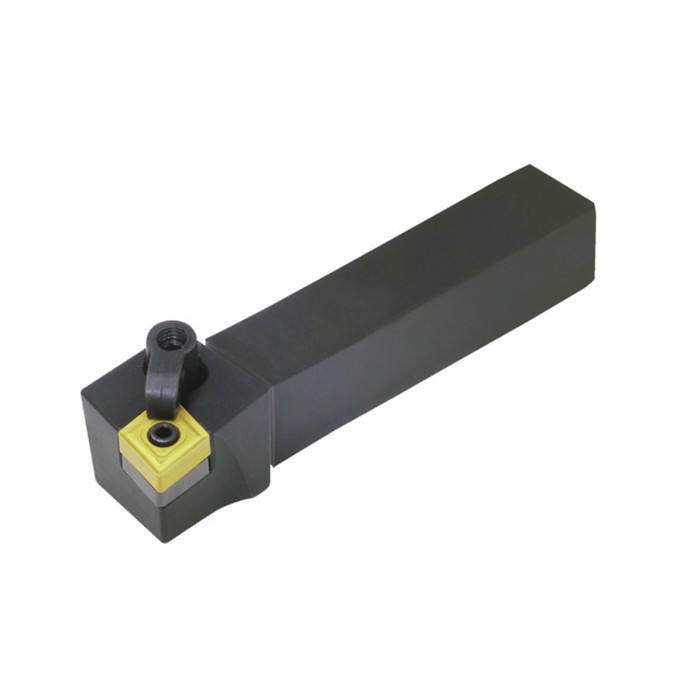 MCLN Indexable Turning Tool Holder With Right And Left Hand
MCLN Indexable Turning Tool Holder With Right And Left Hand -
 Electronic Digital Height Gauge From 300 to 2000mm
Electronic Digital Height Gauge From 300 to 2000mm -
 Precision IP54 Digital Outside Micrometer Of Inch & Metric With Data Output
Precision IP54 Digital Outside Micrometer Of Inch & Metric With Data Output -
 3 Flutes HSS Chamfering Countersink Drill bitl With 60 And 90 Degree
3 Flutes HSS Chamfering Countersink Drill bitl With 60 And 90 Degree -
 Inch HSS 1/2″ Reduce Shank Drill Bit For Metal Cutting Of High Precision
Inch HSS 1/2″ Reduce Shank Drill Bit For Metal Cutting Of High Precision -
 HSS Metric Plain Metal Slitting Saws For Industrial
HSS Metric Plain Metal Slitting Saws For Industrial -
 Precision 5pcs & 6pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type
Precision 5pcs & 6pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type -
 Precision IP54 Digital Caliper With Data Output For Industrial
Precision IP54 Digital Caliper With Data Output For Industrial -
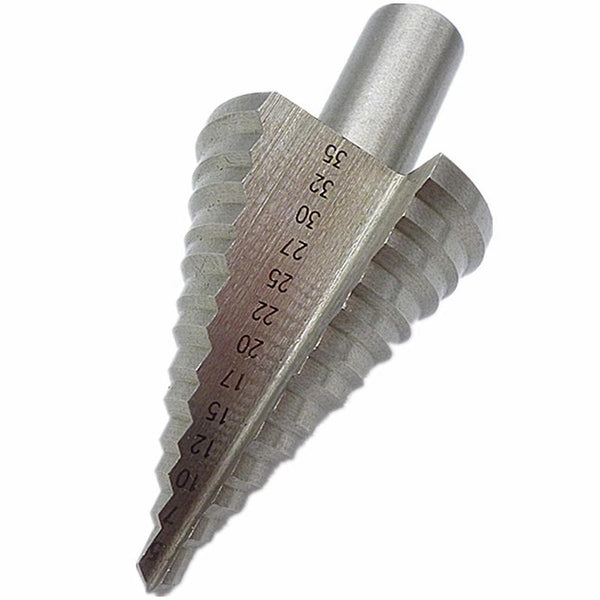 Metric HSS Step Drills With Straight Flute
Metric HSS Step Drills With Straight Flute -
 Precision Digital Bore Guage From 6-450mm Range
Precision Digital Bore Guage From 6-450mm Range -
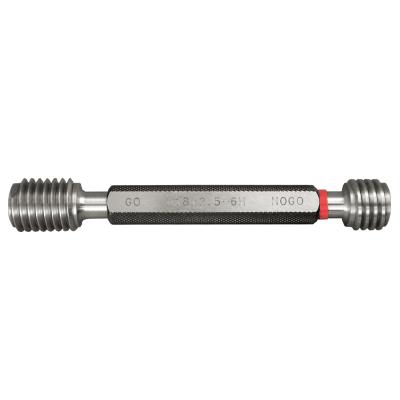 Metric Thread Plug Gauge 6H Accuracy With Go & NO Go
Metric Thread Plug Gauge 6H Accuracy With Go & NO Go -
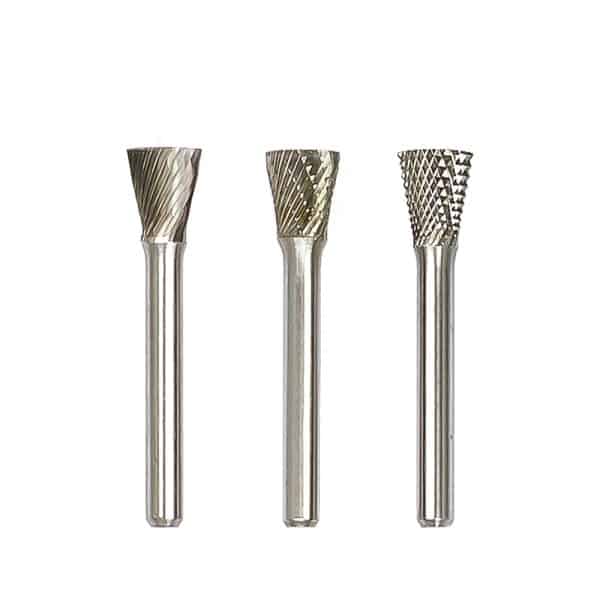 Type N Inverted Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type N Inverted Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr