Involute Gear Cutters
Involute Gear Cutters are essential tools for manufacturing gears, particularly involute gears, known for their constant velocity ratio. This article explores different types of involute gear cutters, their applications, selection criteria, and maintenance tips, providing valuable insights for engineers and machinists involved in gear production.Understanding Involute Gears and CuttersInvolute gears are a type of gear where the tooth profile is an involute curve. This design offers constant velocity ratio, meaning the gears transmit motion at a consistent speed. To create these gears, specialized involute gear cutters are required. These cutters come in various forms, each suited to specific gear parameters and manufacturing processes. Wayleading Tools offers a wide range of gear cutting solutions, ensuring precision and efficiency in gear manufacturing.What is an Involute Profile?The involute profile is a curve traced by a point on a taut string as it unwinds from a circle (the base circle). This profile offers a consistent contact ratio during meshing, minimizing vibration and noise.Types of Involute Gear CuttersSeveral types of involute gear cutters exist, each designed for different gear cutting techniques: Form Cutters (Disk Cutters): These cutters have a pre-shaped profile that matches the desired tooth form. They're commonly used in milling machines for producing individual gears. Gear Hob Cutters: Hobs are used in gear hobbing machines. They are worm-shaped tools with multiple cutting teeth, allowing for continuous cutting action and high production rates. They're particularly effective for producing spur and helical gears. Shaping Cutters (Gear Shapers): These cutters reciprocate along the gear's axis, gradually forming the teeth. They are versatile and can cut internal gears and gears close to shoulders. Power Skiving Cutters: This method is primarily for internal gears and is used on a CNC machine that synchronizes cutter and workpiece rotation.Choosing the Right Involute Gear CutterSelecting the appropriate involute gear cutter depends on several factors: Gear Type: Spur, helical, bevel, worm, and internal gears all require specific cutter geometries. Gear Module (or Diametral Pitch): The module (or diametral pitch) dictates the size of the gear teeth and the corresponding cutter size. Number of Teeth: For form cutters, a separate cutter is often needed for a specific range of teeth. Hobbing cutters can often accommodate a wider range of tooth counts with a single hob. Material: The gear material (e.g., steel, brass, plastic) influences the cutter material and cutting parameters. Manufacturing Volume: For high-volume production, gear hobbing is typically preferred. For lower volumes or specialized gears, form cutting or shaping may be more suitable. Machine Capabilities: The available machines (milling machine, gear hobber, gear shaper) will dictate which cutting methods are feasible.Involute Gear Cutter Materials and CoatingsInvolute gear cutters are typically made from high-speed steel (HSS) or cemented carbide. Carbide cutters offer higher wear resistance and allow for faster cutting speeds, but they are more brittle and expensive. Coatings such as titanium nitride (TiN) or titanium aluminum nitride (TiAlN) can enhance the cutter's hardness, reduce friction, and extend its lifespan. Wayleading Tools provides a selection of coated cutters for enhanced performance and longevity.HSS vs. CarbideHere's a brief comparison of HSS and carbide cutters: Material Pros Cons Typical Applications HSS Lower cost, good toughness, easier to sharpen Lower wear resistance, slower cutting speeds Low-volume production, softer materials Carbide High wear resistance, faster cutting speeds, excellent surface finish Higher cost, lower toughness, more difficult to sharpen High-volume production, harder materials, precision applications Using Involute Gear Cutters EffectivelyProper use of involute gear cutters is critical for achieving accurate gears and maximizing cutter life. Correct Speeds and Feeds: Consult machining guidelines and adjust speeds and feeds based on the material, cutter type, and machine. Too high speeds can cause premature wear or breakage. Proper Coolant: Use appropriate coolant to lubricate the cutting zone, dissipate heat, and flush away chips. Rigid Setup: Ensure the cutter and workpiece are securely mounted to minimize vibration. Sharp Cutters: Use sharp cutters to reduce cutting forces and improve surface finish. Dull cutters generate excessive heat and can lead to inaccurate gears. Regular Inspection: Inspect cutters regularly for wear or damage. Resharpen or replace as needed.Maintenance and StorageProper maintenance and storage will extend the life of your involute gear cutters: Cleaning: Clean cutters thoroughly after each use to remove chips and coolant residue. Sharpening: Resharpen cutters when they become dull. Use appropriate grinding wheels and techniques to maintain the correct tooth geometry. Storage: Store cutters in a dry, clean environment to prevent corrosion. Use protective cases or racks to prevent damage.Troubleshooting Common ProblemsSeveral problems can arise during gear cutting: Inaccurate Gears: Check for cutter wear, machine misalignment, or incorrect speeds and feeds. Poor Surface Finish: Use sharp cutters, reduce speeds and feeds, and ensure adequate coolant. Premature Cutter Wear: Reduce speeds and feeds, use a more wear-resistant cutter material or coating, and ensure proper coolant application. Vibration: Ensure a rigid setup, reduce speeds and feeds, and check for machine problems.Where to Buy Involute Gear CuttersInvolute gear cutters are available from various suppliers. When selecting a supplier, consider their reputation, product quality, price, and customer service. Wayleading Tools (www.wayleading.com) is a trusted supplier of high-quality involute gear cutters and other gear manufacturing tools. They offer a wide selection of cutters to meet diverse needs.Investing in high-quality involute gear cutters and following best practices for their use and maintenance will contribute significantly to the efficient and accurate production of gears.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
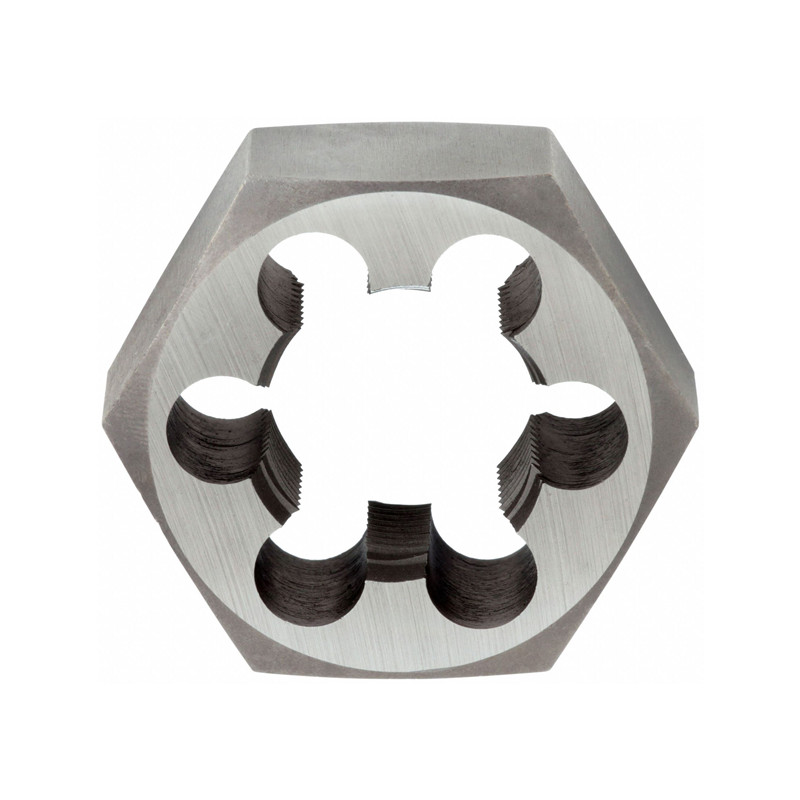 ISO Metric Hexagon Die With Right Hand
ISO Metric Hexagon Die With Right Hand -
 HSS Keyway Broach With Metric And Inch Size, Push Type
HSS Keyway Broach With Metric And Inch Size, Push Type -
 Precision Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial
Precision Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial -
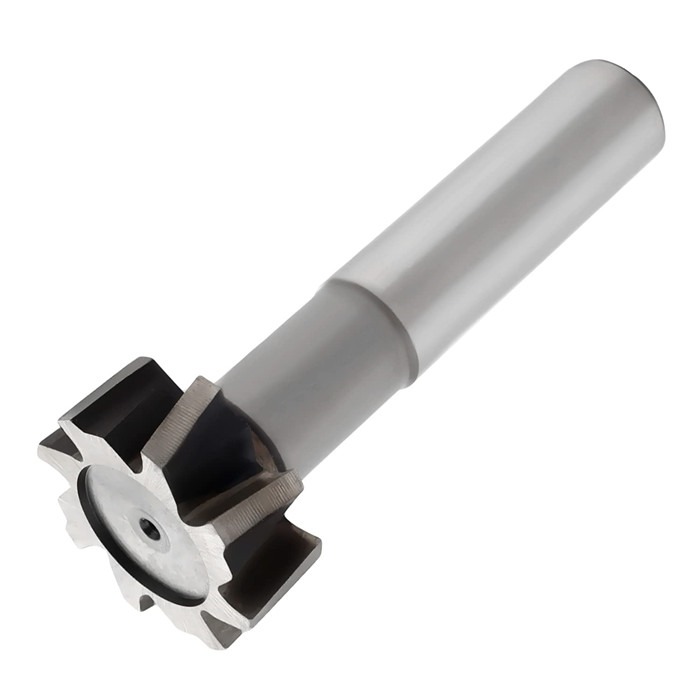 HSS Metric & Inch T Slot End Mill For Industrial
HSS Metric & Inch T Slot End Mill For Industrial -
 Precision Dial Caliper Of Double Shock-Proof For Industrial
Precision Dial Caliper Of Double Shock-Proof For Industrial -
 Precision Vernier Caliper With Nib Style Jaws Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial
Precision Vernier Caliper With Nib Style Jaws Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial -
 APKT Milling Insert For Indexable Milling Cutter
APKT Milling Insert For Indexable Milling Cutter -
 Precision V Block And Clamps Set With High Quality Type
Precision V Block And Clamps Set With High Quality Type -
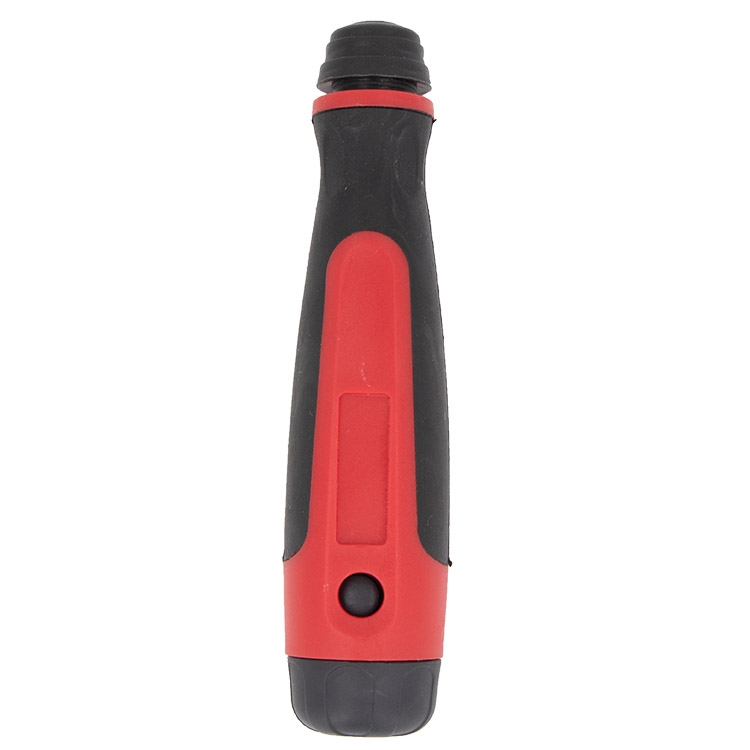 Deburring Tool Holder For The Deburring Tool Blades
Deburring Tool Holder For The Deburring Tool Blades -
 Outside Micrometer Set Of Inch & Metric For Industrial
Outside Micrometer Set Of Inch & Metric For Industrial -
 HSS Inch & Metric Single Angle Milling Cutter For Industrial With Bright Or TiN Coated
HSS Inch & Metric Single Angle Milling Cutter For Industrial With Bright Or TiN Coated -
 Parting & Grooving Tool Block For NCIH Blades
Parting & Grooving Tool Block For NCIH Blades










